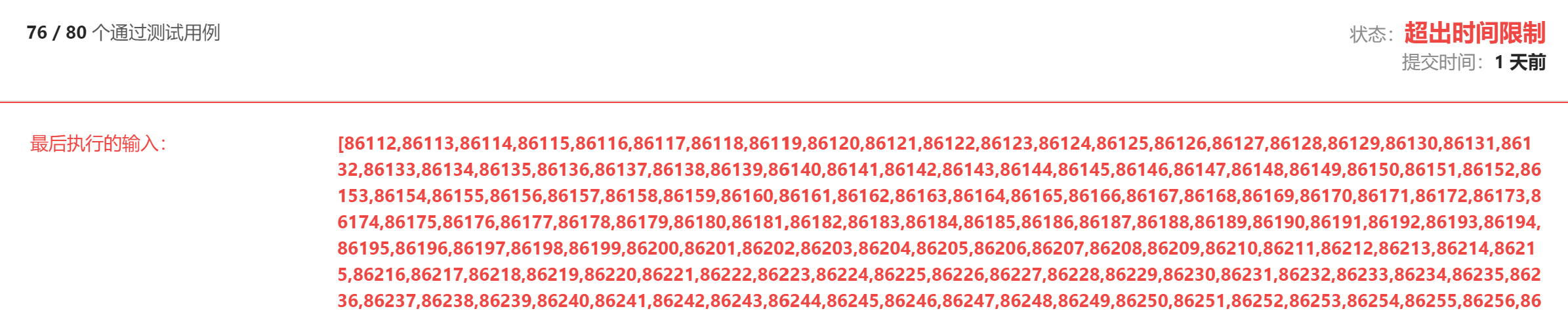
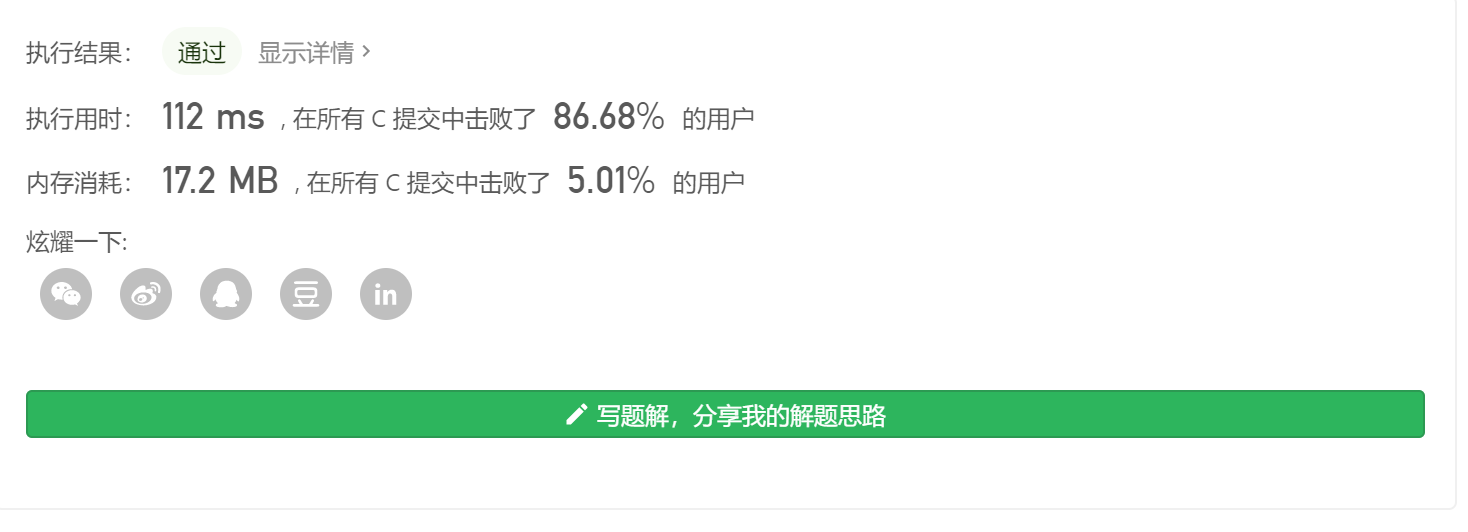
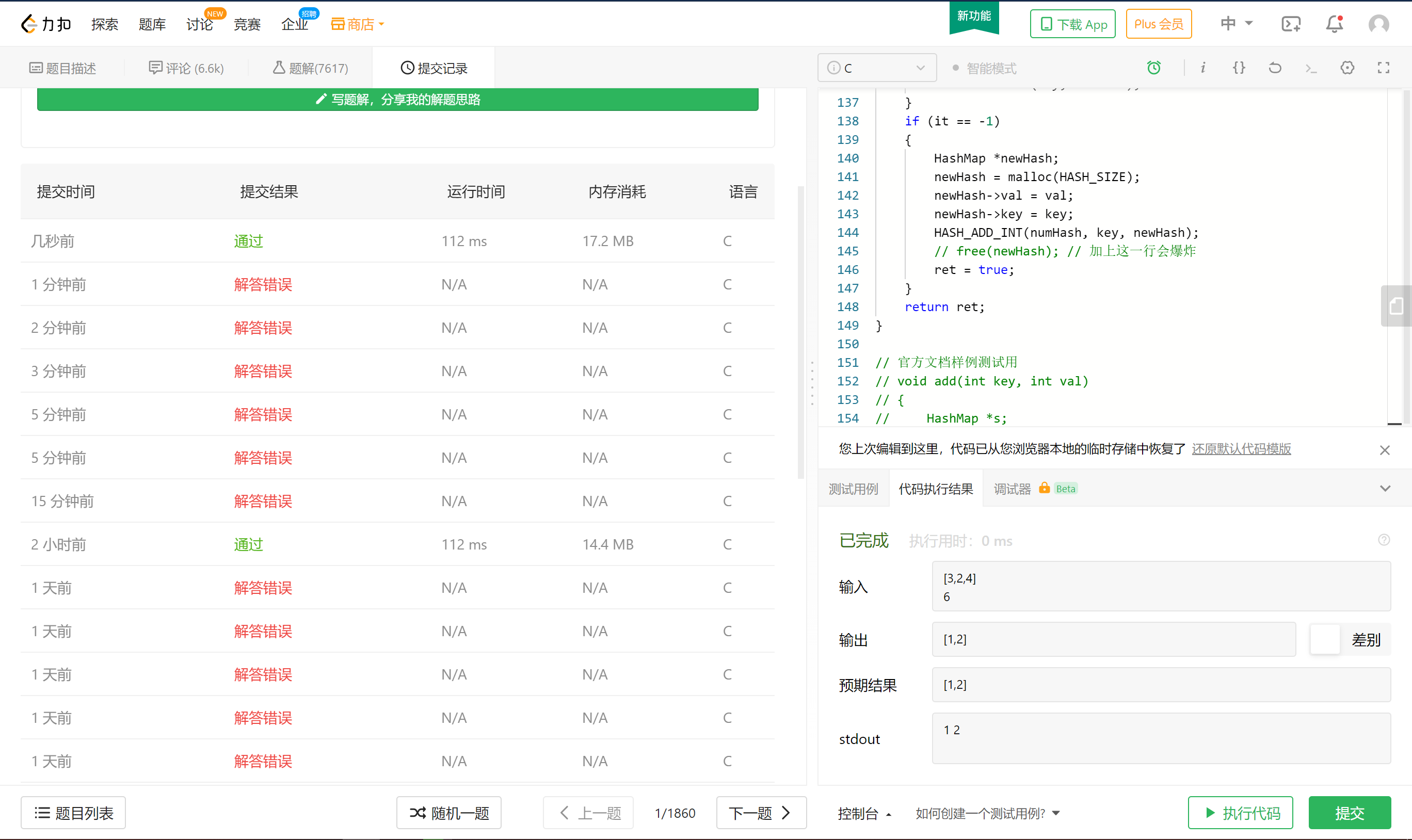
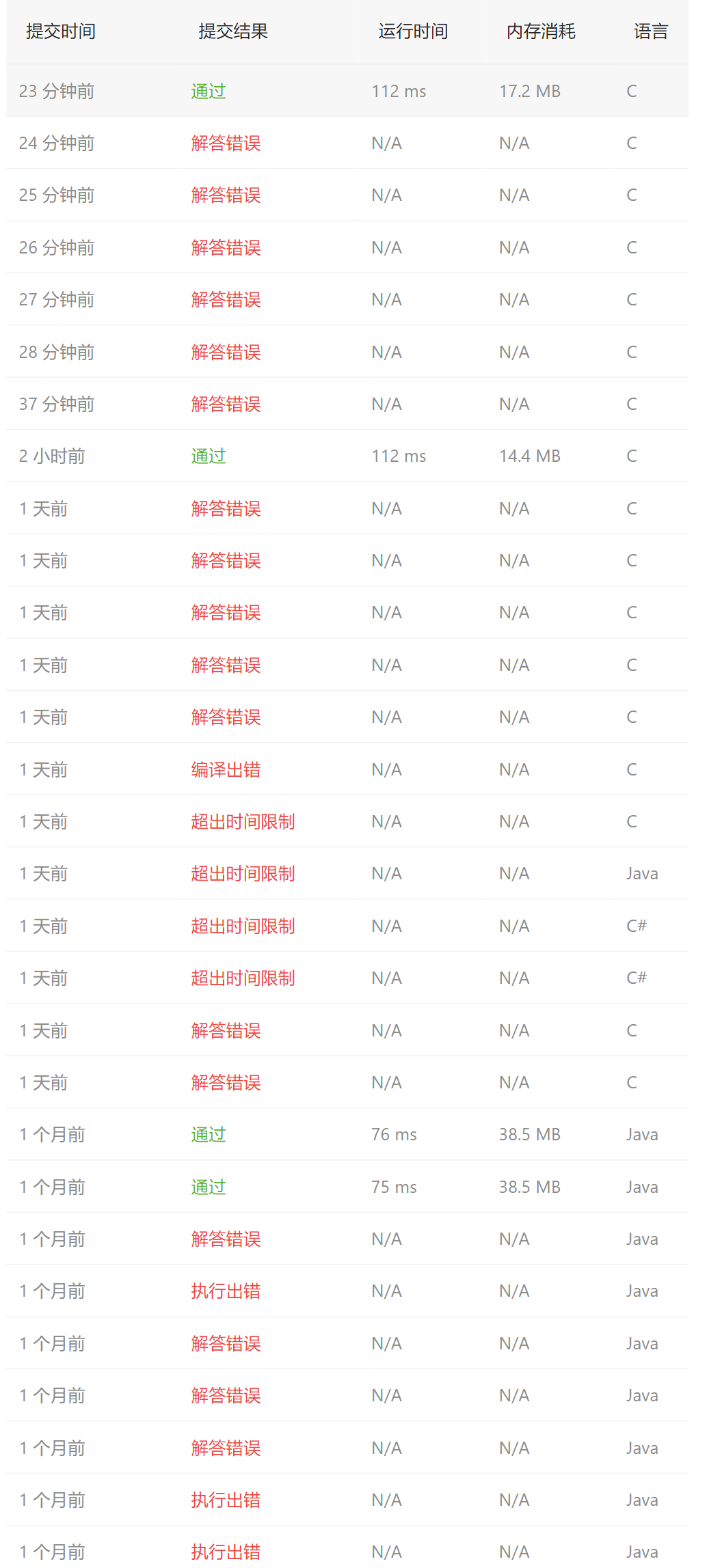
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
| /*AI+移动互联创新实验室 C语言培训练习题 两数之和 | 力扣-1*/
##include <stdio.h>
##include <malloc.h>
##include <math.h>
##include <stdbool.h>
// 头文件
##include "uthash\uthash.h"
##define DEFAULT_SIZE 0
##define FOUND_SIZE 2
##define INT2_SIZE sizeof(int) * 2
// 定义常量 PART1
typedef struct _hashMap
{
int key;
int val;
UT_hash_handle hh;
} HashMap;
// 哈希表结构体
##define HASH_SIZE sizeof(HashMap) * 2
// 定义常量 PART2
int *twoSum(int *nums, int numsSize, int target, int *returnSize);
int hashFind(int key, HashMap *in);
bool hashInsert(int key, int val);
// 函数声明
HashMap *numHash = NULL;
// 新哈希表
int *twoSum(int *nums, int numsSize, int target, int *returnSize)
{
int *ret = NULL;
*returnSize = DEFAULT_SIZE;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; i++, nums++)
{
int other = target - *nums; // 计算另一个orher
int index = hashFind(other, numHash); // 将other作为键寻找
if (index != -1)
{
// 找到则进行返回
ret = (int *)malloc(INT2_SIZE);
*ret = index;
ret[1] = i;
// printf("%d %d\n",index,i );
*returnSize = FOUND_SIZE;
break;
}
else
{
// 未找到则插入数据
hashInsert(*nums, i); // 插入数字作为键,i作为值
}
}
numHash = NULL;
// 置空哈希表,因为在力扣上面是多次运行,而哈希表会保留上次运行的数据
return ret;
// 哈希表查找值
int hashFind(int key, HashMap *in)
{
HashMap *tmp = NULL;
HASH_FIND_INT(in, &key, tmp);
int ret = -1;
if (tmp != NULL)
{
ret = tmp->val;
}
return ret;
}
// 哈希表插入值
bool hashInsert(int key, int val)
{
bool ret = false;
int it = -1;
if (HASH_COUNT(numHash) != 0)
{
it = hashFind(key, numHash);
}
if (it == -1)
{
HashMap *newHash;
newHash = malloc(HASH_SIZE);
newHash->val = val;
newHash->key = key;
HASH_ADD_INT(numHash, key, newHash);
// free(newHash); // 加上这一行会爆炸
ret = true;
}
return ret;
}
|